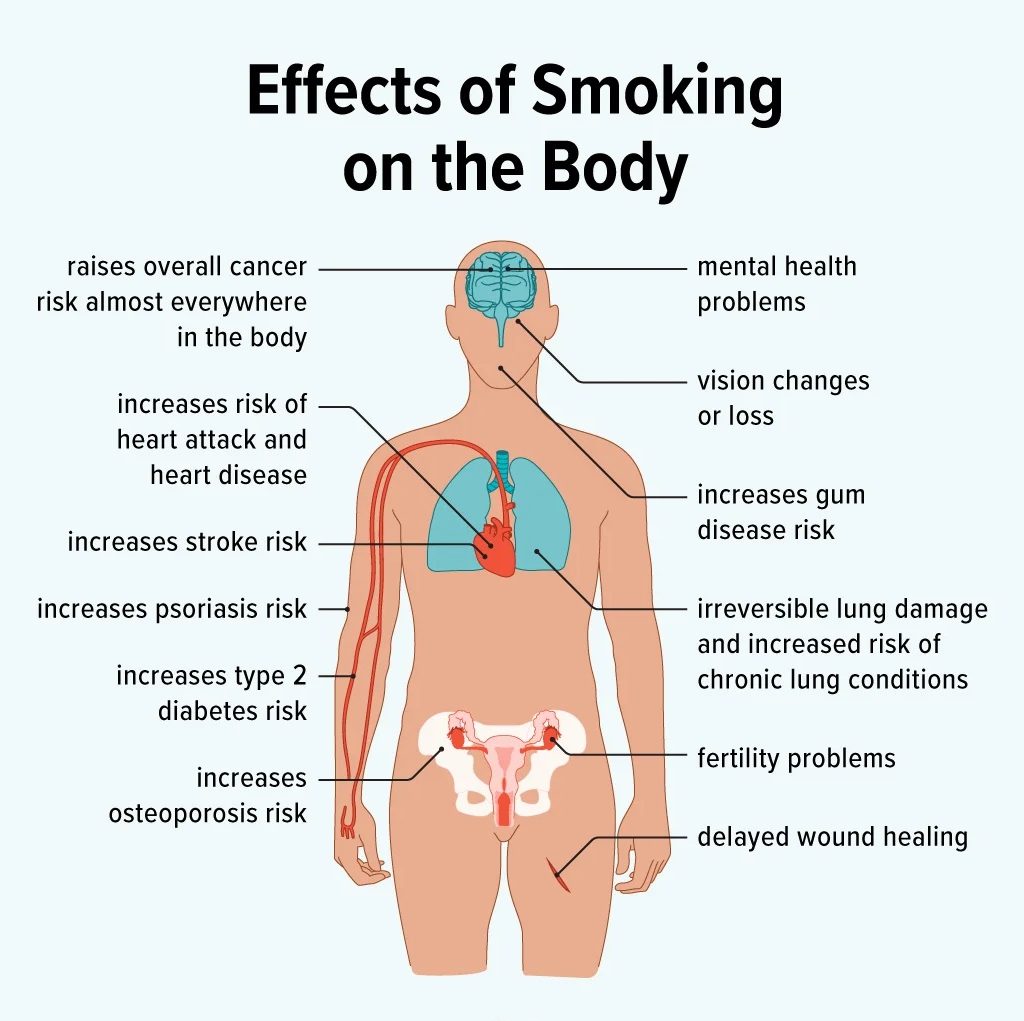
Smoking is one of the leading causes of preventable death in the United States (US). It harms nearly every organ in the body, and the effects can be seen almost immediately after you start smoking.
The effects of smoking can be seen almost immediately after you start smoking. Within minutes of smoking a cigarette, your heart rate and blood pressure increase. Your blood vessels narrow, reducing blood flow to your organs. The tar and other chemicals in cigarette smoke damage your lungs and start to harm your body’s cells.
The longer you smoke, the greater your risk of developing serious health problems. Quitting smoking is the best way to protect your health. When you starting quitting smoking, your body starts to heal itself. Your risk of developing many smoking-related diseases decreases significantly.
In addition to its known cancer risks, smoking also causes many other chronic health problems that need ongoing care. Smoking-related problems that need treatment include:
• Decreased HDL (good) cholesterol and increased blood pressure (increasing risk of heart attack and stroke)
• Erectile dysfunction
• Lower oxygen supply to the heart and other tissues in the body (increasing risks for coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and diabetes)
• Most frequent occurrence of routine illnesses like colds, especially in children living with smokers.
• Poor lung function (ability to get enough oxygen) leading to asthma, bronchitis, or emphysema.
Medical tests that every smoker must get done:
1. Chest X ray: This test is a must for every smoker all over. A chest X-ray can help the pathologists measure the damage that has happened to your lungs so far. Besides, it also helps to gain information about the health of the heart.
2. Spirometry: It is one of the most important tests for smokers. It is a specific kind of breathing test which should be done along with a chest X-ray. This primary test is generally done to measure how effectively your lungs function and therefore to rule out any possibility of lung cancer, lung fibrosis, esophaegal cancer and other interstitial lung diseases. Also known as the PFT test (pulmonary function test), this simple breathing test involves the patient blowing or inhaling into a machine to determine how much air is moving in and out of your lungs.
3. CT Scan: Low-dose computed tomography, or CT scan helps to detect major issues like lung cancer. Chain smokers should never miss out getting a CT scan done, as it provides better diagnostic images, allowing doctors to detect problems, such as lung cancer, in earlier stages than with plain X-rays. Diagnosing lung cancer early can save lives of many, because surgery is often still possible in the early stages. People with stage 1 lung cancers have a 60%-70% survival rate five years after the surgery compared to survival rate of only 5%-30% in later stages.
4. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) test: This is a blood test that finds lower levels of C-reactive protein (CRP and measures general levels of inflammation in your body. The hs-CRP test can be particularly used to find the risk for heart disease and stroke in people who don’t already have a heart disease.In fact, as per a research paper, smokers developed heart disease at a lower hs-CRP level compared with the nonsmokers.
5. Electrocardiogram: Substances such as carbon monoxide in tobacco bind with the haemoglobin in the RBC (Red blood cells) thereby preventing blood from entering your heart. This disrupts the regular functioning of your heart and may also result in clogging blood vessels and blocking arteries. ECG may help health professionals to detect any complications in a smoker’s heart.
6. Diabetes screening: Smoking makes body more resistant to insulin leading to higher levels of blood sugar. Smokers generally have high risk of getting type 2 diabetes which may be the underlying cause for several other problems such as heart and kidney diseases. This is the reason why diabetes screening test is also a must.
7. Vitamin D Blood test: If you are above 40 years of age and are a smoker, then you must go for this test. As a matter of fact, most smokers generally have a low amount of Vitamin D in blood.
How can we prevent smoking?
• Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the harmful effects of smoking, starting at a young age, is crucial. This can be done through school programs, public health campaigns, and media messaging.
• Developing coping skills: Smokers often turn to cigarettes to cope with stress, anxiety, or boredom. Offering alternative coping mechanisms like exercise, relaxation techniques, or social support can help them kick the habit.
• Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT): Patches, gum, and lozenges containing nicotine can ease withdrawal symptoms and cravings, making quitting easier.
• Medication: Certain medications can help reduce cravings and block the pleasurable effects of nicotine, increasing the chances of successful quitting.
• Support groups and counseling: Connecting with others who are trying to quit or with professionals trained in smoking cessation can provide valuable support and guidance.